How to benefit from using Decision Making Software

Image Copyright : rawpixel @123RF
Some people make decisions by intuition rather than by using decision making software support. They don't consider all the options, and so the outcomes are not always successful. Time and money are wasted because the best solution was not chosen first time, rework is need and opportunity can be also lost. For example,
- What business should I start?
- Which product or product improvement to develop next?
- Which is the best lasting solution to a pressing quality of safety problem so the issue does not recur?
- Which candidate to select when recruiting?
- Which software package or product to buy and use?
Problems and opportunities are usually complex and difficult. You usually need to take account of many factors to make the best decision and it is difficult if not impossible to carry all those factors in your head.
Who needs decision making software
Any entrepreneur, business owner, departmental manager, administrator, engineer, scientist, sales or marketing executive, product or service executive, healthcare professional, continuous improvement specialist, or quality improvement executive or safety or risk manager.
How does software improve decision making?
Decision making software usually allows you to document your thinking and decision- making in a visually – so you come to rational or best decisions in a structured and organised way
Good software tools allow you to collaborate and share the decision-making process with your colleagues so you end up with better solutions. ‘Two heads or more are better than one’! This importantly also boosts commitment to the selected solution.
The underlying methods usually found in support software
There a number of underlying approaches in decision support software. Here is a list
- decision matrix,
- prioritization matrix
- decision matrix analysis,
- pugh method or pugh matrix
- lean six sigma pick chart approach
What are the decision making steps
Even when you are using a decision making software tool you need to have an overall methodology
When evaluating an opportunity or solving a problem there is usually an seven-step loop process using a priority matrix approach
1. Identify and define a problem or opportunity or goals not met – write it down
2. Gather the facts, data and information.
3. Analyse and measure the situation – e.g. find causes - ask 5 whys – root cause analysis
4. Generate solutions – brainstorm, or better still ‘brainswarming’ – get all interested parties to write down alone a list of their solutions for consideration so solutions are not pre-judged and eliminated by others
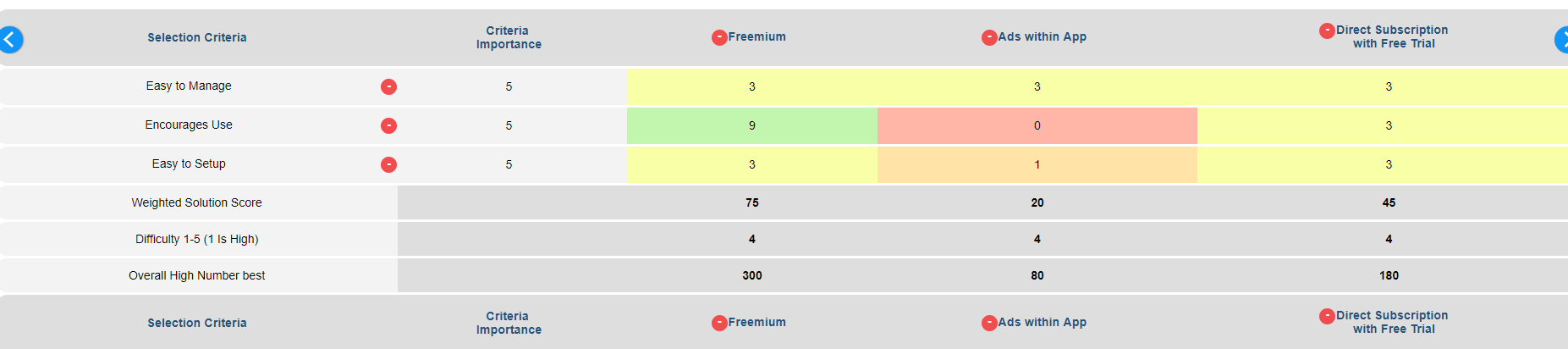
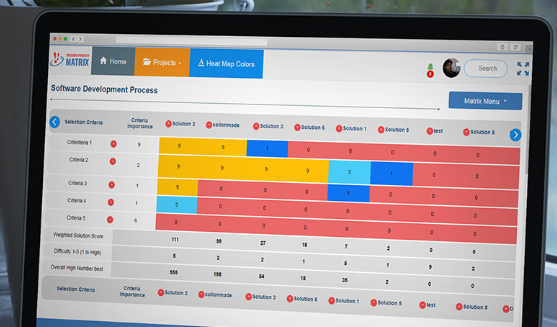
5. Create a basic decision matrix consists of establishing a set of criteria options mapped against potential solutions. See simple example below.
- Each criteria is scored say using a scale from one to five to indicate importance with five being best
- Each solution is also scored on how it meets each criteria.For example with scale 9,3,1,0 with 9 being best
- For each solution you can score how difficult it is to implement using one to five where five is the easiest
- For each criteria-solution on the matrix the scores are multiplied and added to gain a weighted total score for each solution which can then be ranked to give you the best solution.
- Further, you can add an implementation difficulty score say one to five where five is the easiest to implement to multiply the solution weighted score to give the overall best solution score.
- The matrix can rank the solutions either on the weighted scores or overall best solution scores, so you can identify your best solution decision.
See the Forest for the Trees
Find out more about decision making - see the following links:
- Decision Making Software
- Types of Decision Making
- Decision Making Quotes
- Key Decision Making Tips
- Decision Making Models
- Intuitive Decision Making
- Rational Decision Making
- A Better Decision Making Model
- Key Factors in a Decision Making Process
- Use a PICK chart to Simplify Decisions